Big data, data science and machine learning explained
- by 7wData
Data are considered the new secret sauce, are everywhere and have been the cornerstone for the success of many high-tech companies, from Google to Facebook.
But we always used data, there are examples from the ancient times dated thousands of years ago. In the latest centuries data started to find more and more practical applications thanks to the emergence of statistics and later by the Business Intelligence. The earliest known use of the term “Business Intelligence” is by Richard Millar Devens in 1865. Devens used the termto describe how a banker gained profit by receiving and acting upon information about his environment, prior to his competitors.
It is after the WWII that the practice of using data-based systems to improve business decision-making – surely driven by advances in automatic computing systems and storage possibilities – started to take off and be used widely. Digital storage becomes more cost-effective for storing data than paper and since then, an unbelievable amount of data have been collected and organised in data warehouses, initially in structured formats. The term Big Data started to be used meaning just a lot of data.
In a 2001 research report and related lectures, analyst Doug Laney defined data growth challenges and opportunities as being three-dimensional, i.e. increasing
Gartner, and now much of the industry, quickly picked this “3Vs” model for describing Big Data which, a decade later, has become the generally accepted three defining dimensions of big data.
Especially critical is here that the Big Data focus is not primarily about the size but all 3 aspects, the characteristics of the data nonetheless its variety.
Relational Databases require ‘pristine data’. If the data is in the database then it is accurate, clean and 100% reliable. A huge amount of time, money and accountability is put on to making sure the data is well prepared before loading it in to the database.
Big Data tackles this problem from the other direction. The data are poorly defined, much of it may be inaccurate and much of it may in fact be missing. Big Data has to have enough volume so that the amount of bad data or missing data becomes statistically insignificant.
The abundance of available data means also that the trend was shifting from Business Intelligence (inherently descriptive statistics ) where data is used to measure things, detect trends, etc.. to the use of inductive statistics to infer laws from large sets of data to reveal patterns, relationships and dependencies, or to perform predictions of outcomes and behaviours.
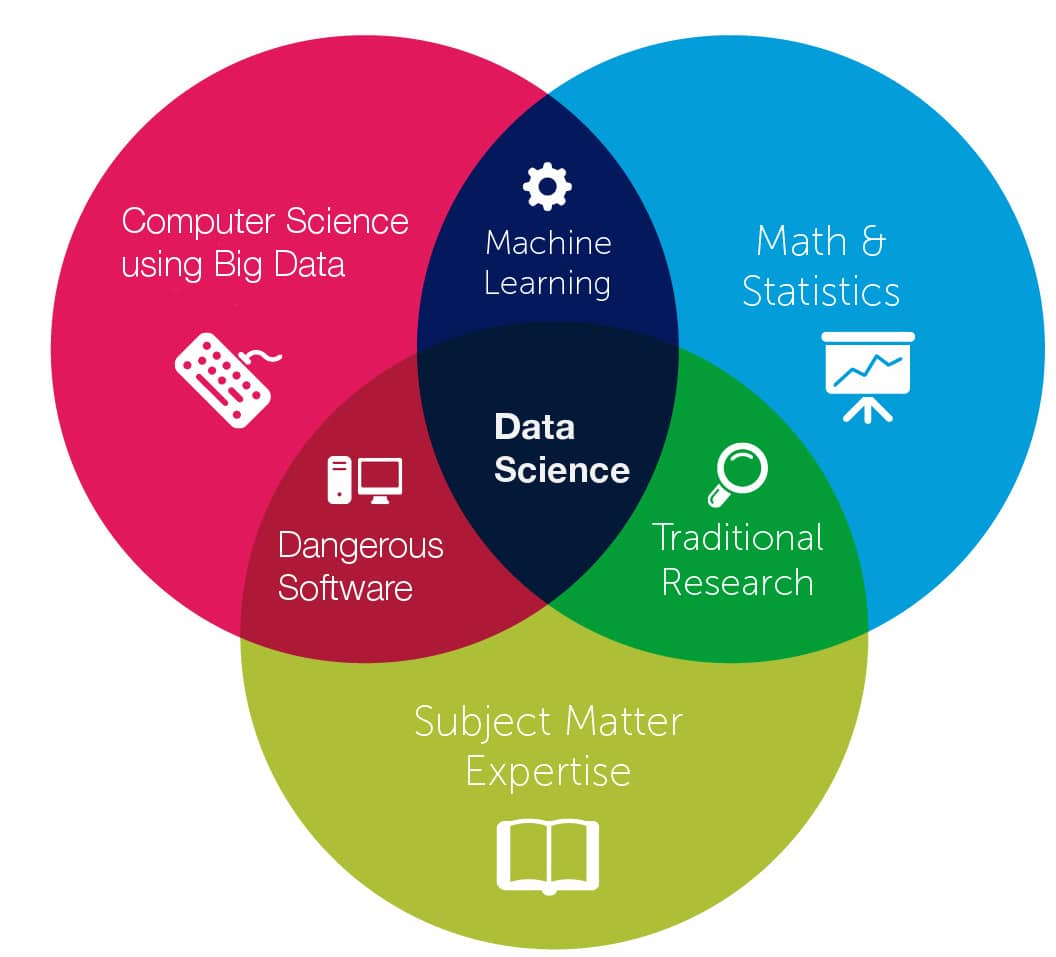
In the world of data this new interdisciplinary field is called data science.
data science is all about extracting knowledge from data, either structured or unstructured, and incorporates many diverse skills such as mathematics, statistics, Artificial Intelligence, computer programming, visualisation, image analysis, and much more.
The term “data science” has existed for over thirty years and was variously used interchangeably for data analysis or data mining (i.e., the process of discovering patterns in large data sets, like when you mine a mountain of data and your goal is to find the nuggets of insight) but gradually started to include more areas.
Don’t be fooled by the many academics and journalists who see no distinction between data science and statistics or even advocate that statistics be renamed data science and statisticians data scientists (C.F. Jeff Wu in 1997).
Data science is an independent discipline, who relies on the shoulders of statistics but it is extending the field to new realms thanks to Big Data, Computer Science and distributed systems.
[Social9_Share class=”s9-widget-wrapper”]
Upcoming Events
Evolving Your Data Architecture for Trustworthy Generative AI
18 April 2024
5 PM CET – 6 PM CET
Read MoreShift Difficult Problems Left with Graph Analysis on Streaming Data
29 April 2024
12 PM ET – 1 PM ET
Read More